Exercise Stress Test (EST)
diagnosis
table of contents
What is an Exercise Stress Test?
What do we use stress test for?
What are the types of stress tests?
How should the patient prepare for the Exercise Stress Test?
What if the patient have diabetes?
What happens during the Exercise Stress Test?
After Test
Risks
Results
Exercise stress test at Bangkok Heart Hospital and Bangkok Hospital at Headquater
What is an Exercise Stress Test?
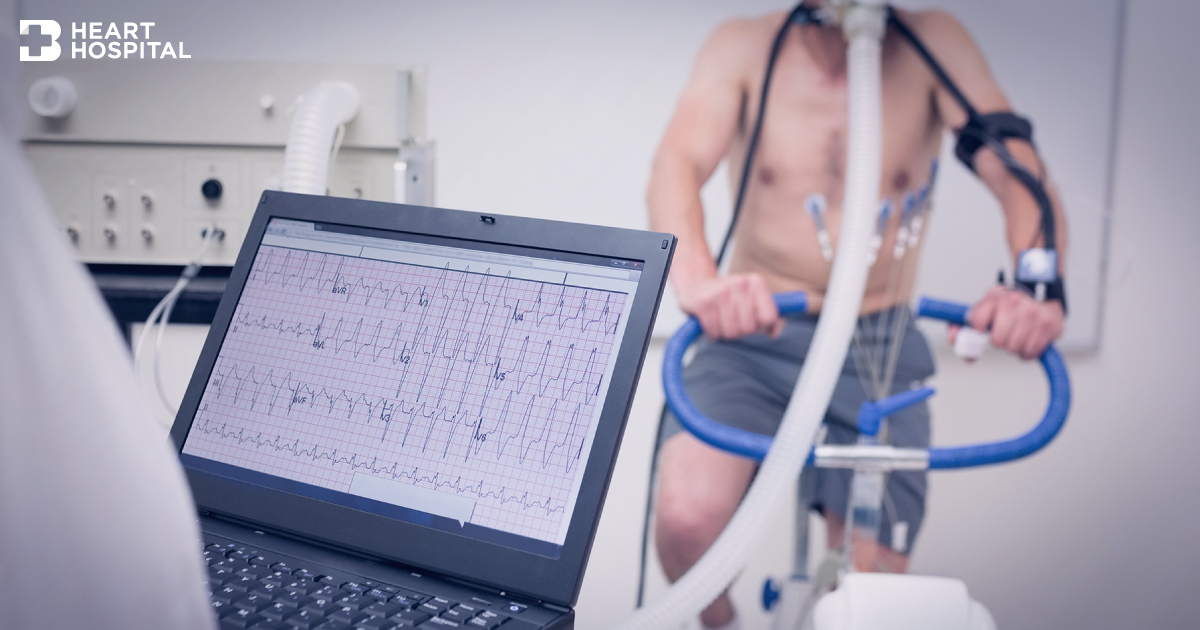
The exercise stress test also called a stress test, graded exercise test (GXT), or treadmill test, is used to provide information about how the heart responds to exertion. It usually involves walking on a treadmill (at Bangkok Heart Hospital) or pedaling a stationary bike at increasing levels of difficulty, while your symptoms, electrocardiogram, heart rate, and blood pressure are monitored.
A stress test can help diagnosis of heart disease. Stress tests are performed by trained technician under supervision of a doctor, to determine the amount of stress that your heart can manage before developing significant symptoms or abnormal ECG or evidence of ischemia (not enough blood flow to the heart muscle).
What do we use stress test for?
- To evaluate symptoms of chest discomfort, short of breath, fatigue.
- To determine if there is adequate blood flow to the heart muscle during increasing levels of activity.
- To determine the likelihood of having coronary heart disease and the need for further evaluation.
- To check the effectiveness of procedures done to improve blood flow within the heart vessels in people with coronary heart disease.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of the heart medications to control angina and ischemia.
- To evaluate abnormal heart rhythms.
- To assess the patient exercise capacity
- Help determine a safe exercise program.To help predict risk of heart related conditions.
What are the types of stress tests?
- Treadmill stress test: As long as the patient can walk and have an acceptable ECG, this is normally the first stress test recommended. The patient walks on a treadmill while being monitored to see how far he/she can walk and if he/she develops chest pain or changes in ECG that suggest that the heart muscle is not getting enough blood.
- Stress echocardiogram: This test combines treadmill stress test and echocardiogram which can give diagnosis of certain heart conditions more accurate. A stress echo allows visualization of the motion of the heart’s walls and pumping action when the heart is stressed. It may reveal a lack of blood flow to the heart muscle that is not apparent at rest.
- Dobutamine stress test: This test is used in people who are unable to exercise. A drug is given intravenously to make the heart respond as if the person were exercising. This way the doctor can still determine how the heart responds to stress, but no exercise is required. The test is performed with imaging test such as echocardiogram while dobutamine is given intravenously.
- Nuclear stress test: This test help determine which parts of the heart muscle receive adequate blood supply and if the heart pumping chamber is healthy and function normally or not. A small amount of radioactive substance is injected into the patient. There is a special camera to record the picture of radioisotope distribution to the heart muscle. These pictures are done both at rest and after exercise for comparison.
How should the patient prepare for the Exercise Stress Test?
Before your stress test:
- Do not eat or drink anything except water for 3 hours before the test.
- Do not drink or eat foods containing caffeine for 12 hours before the test. Caffeine will interfere with the results of the test.
- Check with the doctor or nurse which medication should be withheld on the test day. If the patient use an inhaler for breathing, bring it to the test day.
- Prepare for soft-soled shoes suitable for walking and comfortable clothes.
- Do not bring values items
- Comfortable shoes and socks are provided in case you do not have it with you or your test day.
What if the patient have diabetes?
Ask the doctor or scheduling nurse how to prepare for the test.
What happens during the Exercise Stress Test?
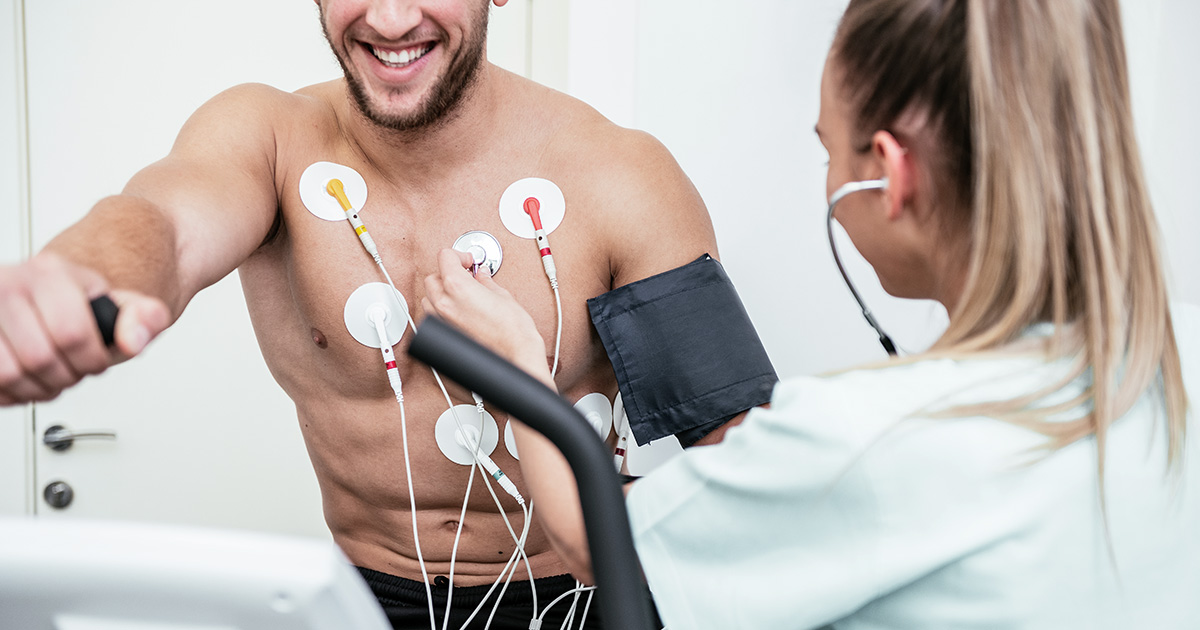
First, during a stress test, a technician will gently clean 10 small areas on your chest and place electrodes (small, flat, sticky patches) on these areas. The electrodes are attached to an electrocardiograph monitor (ECG or EKG) that charts the heart’s electrical activity during the test.
Before the patient start exercising, the technician will perform an ECG to measure the heart rate at rest and will take the blood pressure. Patient will begin to exercise by walking on a treadmill (at Bangkok Heart Hospital) or pedaling a stationary bicycle. The rate of exercise or degree of difficulty will gradually increase. The patient will be asked to exercise until he/she feels near exhausted. The doctor may stop the test when the patient heart rate reach adequate level or if the patient develops symptom of chest, arm, or jaw pain or discomfort, short of breath, dizzy, lightheaded, or any other unusual symptoms. At regular intervals, the lab personnel will ask how the patient are feeling. The lab personnel will watch for any symptoms or changes on the ECG monitor that suggest the test should be stopped. It is normal for the heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and respiration to increase during the test. After the test the patient will walk slowly for a short period of time to cool down. Your heart rate, blood pressure and ECG will continue to be monitored until the levels begin returning to normal. The actual exercise time is usually between 6 and 12 minutes but the total time for complete the exercise stress test is about 45 to 60 minutes. (Time for different type of stress test varies).
After Test
You may resume normal activities.
Risks
Stress tests are mostly safe, but all procedures have some risk. Your doctor will review potential problems.
- Shortness of breath is usual symptom of exercise.
- You may experience chest pain if you have significant coronary artery disease.
- Some may have musculoskeletal discomfort.
- Low blood pressure is uncommon risks and complications (1 – 5%).
- Rare risks and complications (less than 1%) include fainting, arrhythmia.
- Heart attack is extremely rare.
Technicians will be alert for any signs of heart or lung problems. Immediate action will be taken if complications happen. A doctor, most often a cardiologist, will be available during the stress test as well.
Results
The doctor will review the test results and send a report to your doctor. The report is often sent within 24 hours.
One or more of the following are considered a positive (abnormal) stress test:
- ECG changes that show low oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- You develop chest pain or trouble breathing, especially if associated with ECG changes.
- Failure to properly increase heart rate and/or blood pressure during exercise.
The test might suggest that you have a heart condition or not. Your doctor may do more tests to confirm the diagnosis. Talk to your doctor about your results.
Exercise stress test at Bangkok Heart Hospital and Bangkok Hospital at Headquater
- Stress tests include exercise treadmill stress test and pharmacologic stress test
- High number of exercise stress tests are from the popular checkup program which include exercise stress test for functional and diagnostic evaluation
- Number of exercise stress test and exercise echo stress test done at Bangkok Heart Hospital: