Echocardiogram
diagnosis
table of contents
What is it?
How does it work?
What does it show?
The different types of Echocardiogram
How is it done?
Pre-procedure preparation
Risks
Results
Echocardiogram at Bangkok Heart Hospital
What is it?
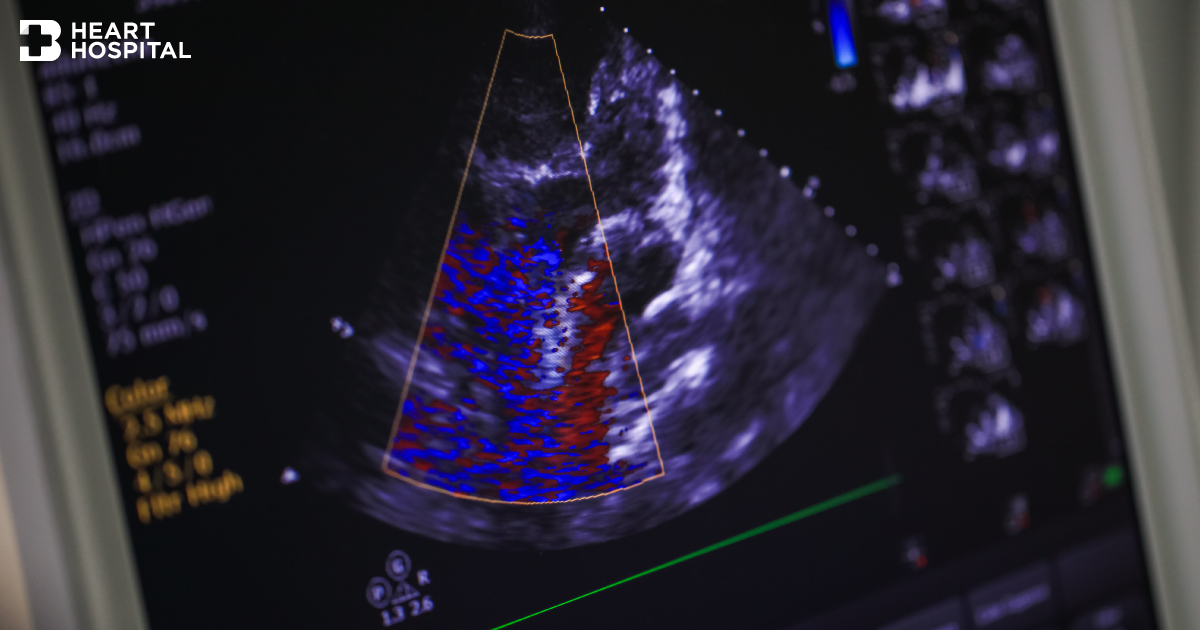
An echocardiogram, or ultrasound of the heart, is a noninvasive test that uses ultrasound technology to provide a picture of the structures of the heart.
How does it work?
A transducer applying on the chest wall transmits high frequency sound into the chest. This ultrasound wave will bounce off the walls and valves of the heart. The sound waves return to the transducer as echoes, which are then converted into moving images of your beating heart and its valves as they open and close
What does it show?
- The size of the four heart chambers and their function.
- The strength and wall motion of the pumping chamber due to inadequate blood supply of the heart muscle, or a heart attack.
- The heart valves abnormality.
- Abnormal structures in the heart such as blood clot or tumor or infectious growth around the heart valves.
- Problems with the outer lining of your heart (the pericardium).
- Problems with the large blood vessels that leave the heart (aorta)
- Abnormal holes between the chambers of the heart (congenital heart disease)
By adding Doppler ultrasound to the equipment, we can get good picture of direction and speed of the blood flows through the heart and great vessels such as aorta.
The different types of Echocardiogram
- Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE). This is the most common type. Views of the heart are obtained by moving the transducer to different locations on your chest or abdominal wall.
- Stress echocardiogram. A stress echocardiogram is usually done to find out if you might have decreased blood flow to your heart muscle (coronary artery disease).
- Doppler echocardiogram. This test is used to look at how blood flows through the heart chambers, heart valves, and blood vessels.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE). For this test, the probe is passed down the esophagus instead of being moved over the outside of the chest wall. TEE shows clearer pictures of the heart, because the probe is located closer to the heart and because the lungs and bones of the chest wall do not block the sound waves produced by the probe.
- Three dimensional echocardiogram. Using special probe and software, the echocardiographic image can be displayed in a 3D format.
How is it done?
An echocardiogram may be done in a hospital, clinic, or doctor’s office. It can also be done at the bedside in the hospital.
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and Doppler echocardiogram
- The patient will lie on your back or on your left side on a bed or table. A small instrument (transducer) that looks like a microphone, covered with gel, is pressed firmly against the chest wall and moved slowly back and forth. This instrument sends sound waves into the chest and picks up the echoes as they reflect off different parts of the heart. The echoes are sent to a video monitor that records pictures of your heart for later viewing and evaluation.
- The test usually takes from 20 to 40 minutes.

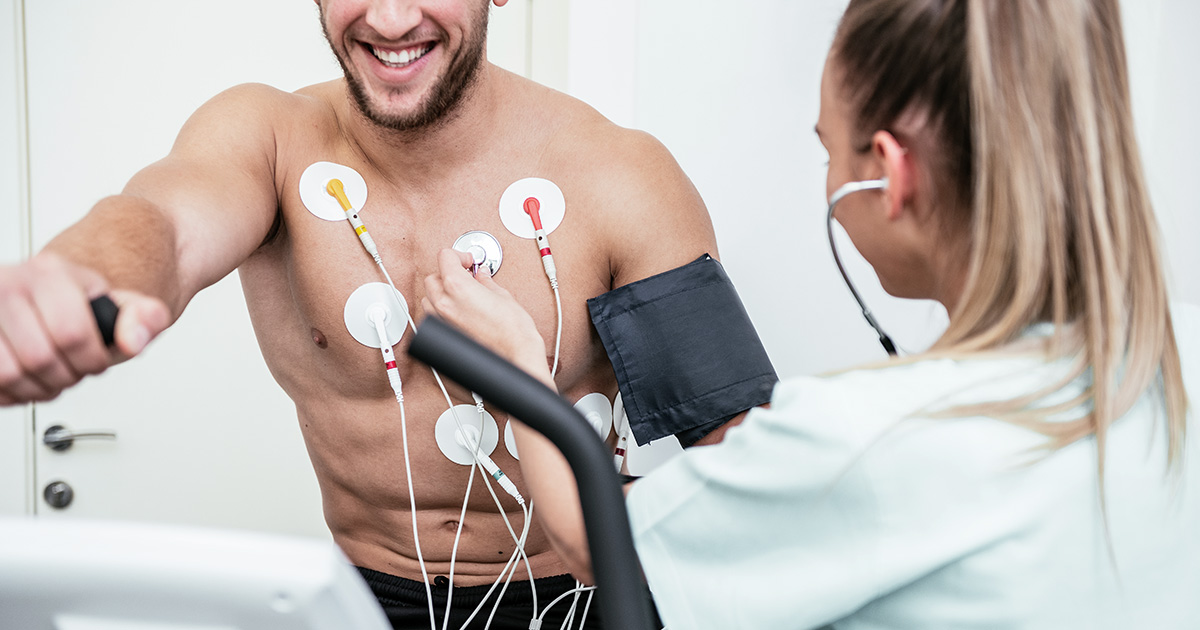
Exercise stress echocardiogram
- Echocardiogram (TTE type) will be done before and immediately after exercise (usually walk on the treadmill).
- An exercise stress echo takes about 45 to 60 minutes.
Dobutamine stress echocardiogram
- In patient who cannot walk adequately, medicine called dobutamine is used instead of exercise to stress the heart. Dobutamine will be given intravenously to make the heart work harder like exercise. Echocardiogram images will be taken while you receive the dobutamine intravenously. A dobutamine stress echo takes about an hour.
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
- Before the test, medicine to decrease saliva and stomach secretions and sedative to relax the patient. The throat may be numbed with an anesthetic spray to ease insertion of the probe.
- The test takes about 20 to 40 minutes

Pre-procedure preparation
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and Doppler echocardiogram
- You do not need any special preparation for a transthoracic or Doppler echocardiogram.
Stress echocardiogram
- Do not eat or drink for 3 hours before a stress echo. The patient may feel nauseated if exercise with a full stomach or from the injection of dobutamine.
- Wear flat, comfortable shoes (like tennis or walking shoes) and lightweight shorts or sweatpants.
- Ask your doctor whether you should take your regular medicines as usual. Tell your doctor if you take insulin or diabetic medicine.
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
- Do not eat or drink for at least 6 hours before the TEE.
- If the patient has dentures or dental prostheses, they may need to be removed before the test.
- If you have medical problems involving the throat, esophagus, or stomach, tell your doctor before getting this test.
- Before a TEE, you will be given a sedative. You will not be able to drive for at least 12 hours after the procedure. Be sure to make arrangements in advance for someone to pick you up after the test.
Risks
- An echocardiogram is safe, because the test uses only high frequency sound waves that have not been shown to have any harmful effects
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) and Doppler echocardiogram
- There are no known risks from a transthoracic or Doppler echocardiogram. During a transthoracic echo, the technician may have to press hard on your chest with the transducer. Tell the technician if you feel any pain or discomfort.
Stress echocardiogram
- A stress echocardiogram can cause dizziness, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, nausea, irregular heartbeats, and heart attack which is very rare. These symptoms are from the exercise part and not from the echocardiogram part
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
- Nausea.
- Mouth and throat discomfort.
- Minor bleeding.
- Trouble breathing.
- Slow or abnormal heartbeats.
- Insertion of the probe may cause esophageal damage. This is rare.
TEE is not recommended if you have:
- Recently had radiation treatment to the neck or chest.
- Serious problems with your esophagus, such as a very narrow esophagus, dilated (engorged) veins in the esophagus that could rupture and bleed (esophageal varices), or severe arthritis of your neck.
- Trouble swallowing.
- A bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia or anticoagulation medicine.
Results
Results are usually available within one day.
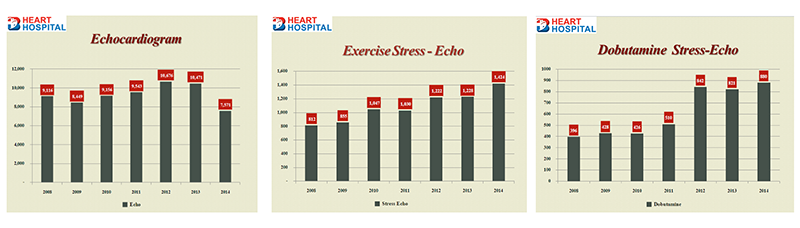
Echocardiogram at Bangkok Heart Hospital
- Routine echo cardiogram is the M-mode, Dlopper and 2 dimensional technique
- Stress echocardiographic tests include exercise treadmill stress echo and dobutamine stress echo
- Specific cases of 3 dimensional and strain are available
- Number performed at Bangkok Heart Hospital yearly