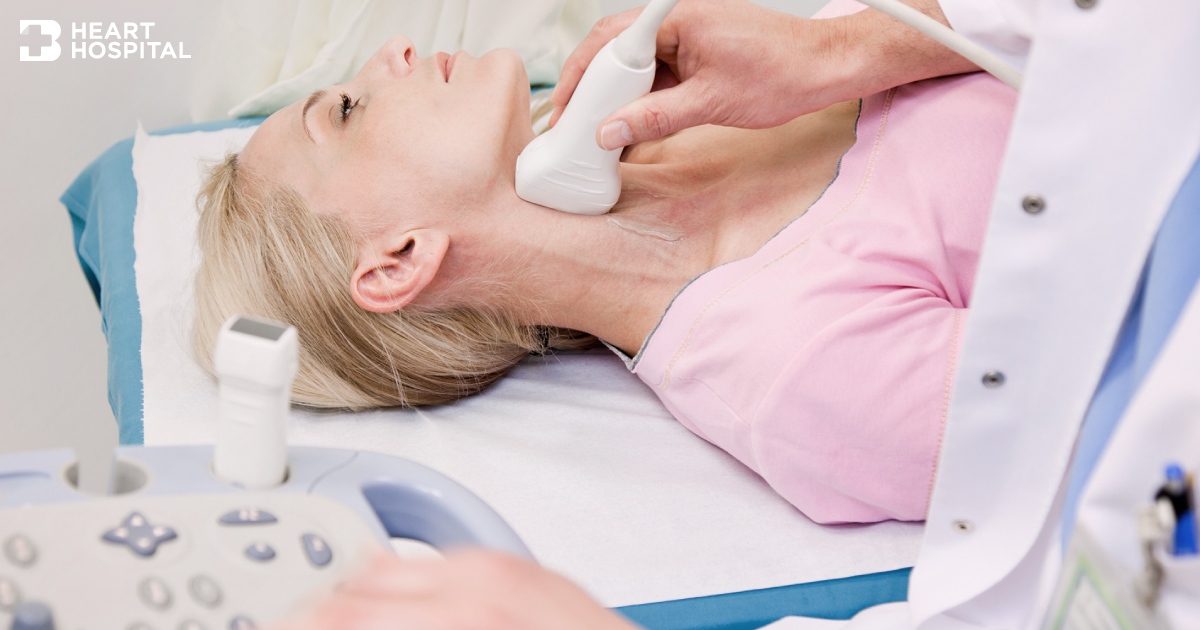
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound Test
diagnosis
table of contents
What is Carotid Duplex Ultrasound Test?
Hypertension Indication
Preparation
Equipment
During procedure
Interpretation
After the test
Alternative
Treatment of carotid (atherosclerotic) and hypertension disease
What is Carotid Duplex Ultrasound Test?
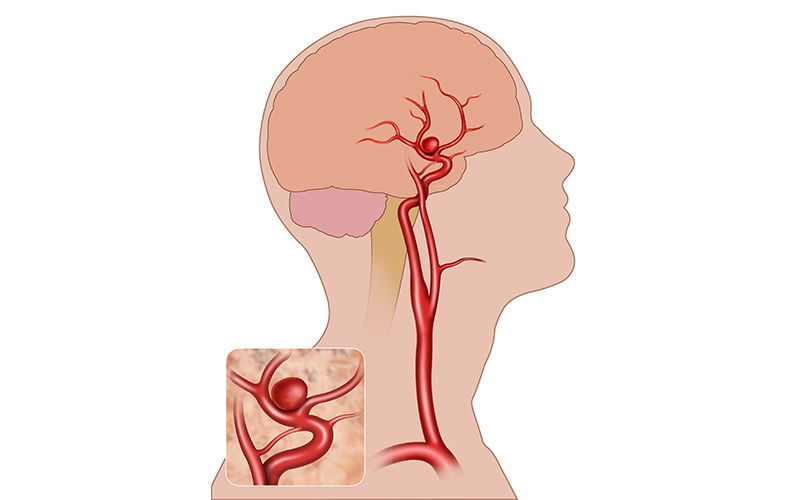
When plaque builds up in the carotid arteries, it is called carotid artery disease. Sometimes, known as hypertension. The hypertension means abnormally high blood pressure. A state of great psychological stress. According to the Society for Vascular Surgery, about one percent of adults ages 50 to 59 have carotid artery disease and hypertension, and 10 percent of adult ages 80 to 89 have it (2010).
A duplex ultrasound combines traditional ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound.
- Traditional ultrasound uses sound waves that bounce off blood vessels to create pictures or image.
- Doppler ultrasound records sound waves reflecting off moving objects, such as blood, to measure their speed and other aspects of how they flow (hypertension).
Carotid Duplex ultrasound is the test for carotid arteries and hypertension that supply blood to the brain. As with other ultrasound examinations, the carotid duplex ultrasound test is safe, non-invasive, painless test and no radiation risk.

Hypertension Indication
- Screening for carotid artery (common, internal and external carotid artery and well as vertebral artery, hypertension) disease in high risk patient
- History of cardiovascular disease.
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Elevated blood cholesterol
- Smoker
- Family history of stroke or heart disease
- Obesity
- Inactive
- History of TIAs or stroke and hypertension
- Assessing the presence, amount, and location of arterial plaque. Plaque in the carotid arteries can reduce blood flow to the brain and may increase the risk of stroke and hypertension.
- Presence of carotid bruit (abnormal sound over carotid artery which usually indicate carotid artery narrowing and hypertension).
- Pre-op examination before major cardiovascular surgery such as CABG.
- Using Intimal Media Thickening (IMT) of carotid artery for risk estimation of developing cardiovascular events such as heart attack or stroke.
- Check the position of a metal stent placement to maintain carotid blood flow.
Preparation
- Wear comfortable, loose and open necked clothing.
- Remove all clothing and jewelry in the area to be examined.
- No smoking for few hours. Cigarette smoking cause artery constriction.
Equipment
- Ultrasound scanner
- Transducer
- Clear water-based gel
During procedure
Patient will be asked to lie down supine with a pillow underneath your head for support. The test is performed on both sides of your neck. The face will be turned to the opposite side of examination. The technician will apple gel over the examining area to facilitate better sound traveling. The transducer will move back and forth over the carotid artery to obtain image and Doppler signal. You may hear a whooshing sound, which is the sound that the ultrasound machine makes to represent your blood moving through the blood vessel. Once the procedure has been completed, the gel will be wiped off. The results are compared to standard values to determine the amount of blockage or narrowing of the arteries to prevent hypertension.
Interpretation
A consensus conference in 2003 of the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound recommended the following criteria for estimating stenosis and to aviod hypertension:
- Normal: ICA PSV < 125 cm/s and no plaque or intimal thickening is visible.
- < 50% stenosis: ICA PSV < 125 cm/s and plaque or intimal thickening is visible.
- 50-69% stenosis: ICA PSV is 125-230 cm/s and plaque is visible.
- >70% stenosis to near occlusion: ICA PSV >230 cm/s and visible plaque and lumen narrowing are seen.
After the test
There is no special type of care required after a carotid artery duplex scan. You may resume your usual diet and activities unless your doctor advises you differently.
Alternative
- Carotid MRI/MRA
- Carotid CT
- Carotid angiogram
Treatment of carotid (atherosclerotic) and hypertension disease
- Medical
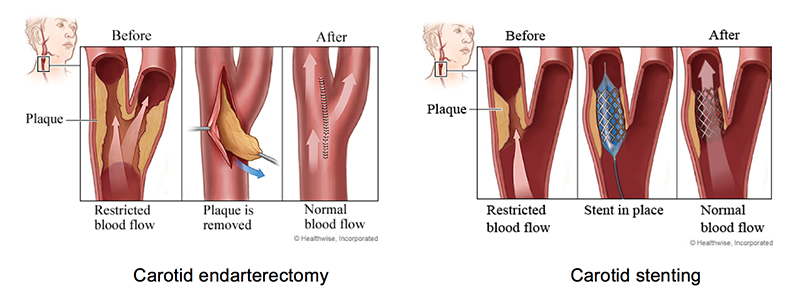
- Surgery (Carotid endarterectomy)
- Carotid angioplasty – Carotid stenting