256-Slice Multi Detector CT Scan
diagnosis
table of contents
What is a CTA or Coronary CTA?
What methods are used by CT scanning to detect plaque in the arteries?
What is the traditional method to look at the coronary arteries?
What is the advantage of Coronary CTA over catheter-based angiography?
Why is a 256 slice CT scanner better than a 64 slice CT scanner? (Bangkok Heart Hospital Equips with the state of the art 256 slice CT scanner)
What is the difference between Coronary CTA, nuclear stress test and Exercise Stress Testing?
What are the clinical indications to have a Coronary CTA?
Are there any risks involved with the exam?
What health conditions should you inform the doctor of before the test?
Is there any preparation for the test?
How is the procedure performed?
How long does the procedure take?
After the test
What is a CTA or Coronary CTA?
Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA) is an imaging exam that uses a CAT (Computerized Axial Tomography) scanner to examine the cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels in various parts of the body). After intravenous contrast injection in an arm vein, this highly specialized procedure utilizes x-rays to acquire axial images, which are then assembled into three-dimensional views of the blood vessels using state-of-the-art computer software. When used to view the arteries of the heart, this exam is referred to as coronary CTA.
A CT scanner looks like a big doughnut. The patient aperture (opening) is 60 cm to 70 cm (24″ to 28″) in diameter. Inside the covers of the CT scanner is a rotating frame which has an x-ray tube mounted on one side and the detector mounted on the opposite side. A fan beam of x-ray (see the above figure) is created as the rotating frame spins the x-ray tube and detector around the patient (see figure below). Each time the x-ray tube and detector make a 360° rotation, an image or “slice” has been acquired. This “slice” is collimated (focused) to a thickness as thin as 1 mm
What methods are used by CT scanning to detect plaque in the arteries?
There are two methods of plaque detection with CT scanning of the heart:
- Coronary Calcium Scoring: Coronary Calcium Scoring is a noninvasive test that can detect the presence and severity of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries. This is a powerful predictor of the risk of a heart attack.
- Coronary CTA: Coronary CTA is the definitive method for evaluating all the coronary plaque (calcified and non-calcified) and also used to determine if there are narrowing or blockages in the coronary arteries. In addition, cardiac function or how well the heart is pumping can be calculated.
What is the traditional method to look at the coronary arteries?
Traditionally, catheter-based angiography (coronary angiogram) has been used to evaluate the coronary arteries. In this invasive procedure, a long thin tube over a wire is threaded through the groin or wrist arteries to the heart where dye or contrast media is injected directly into the arteries and viewed under x-ray video screen. Although this procedure carries risks, it is still considered to be a very valuable test for those who present with symptoms of acute chest pain or heart attack or those who will require coronary intervention or surgery.
What is the advantage of Coronary CTA over catheter-based angiography?
- CTA is a noninvasive procedure. Not only does it visualize the coronary arteries and identify narrowing or blockages, but it also shows the plaque in the artery wall that catheter-based angiography cannot detect.
- The calcified plaque can be measured and used to predict the risk of a heart attack.
- CT angiography can easily detect other dangerous causes of chest pain, such as:
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot to the lungs).
- Dissection of the aorta, the main blood vessel that leaves the heart.
Why is a 256 slice CT scanner better than a 64 slice CT scanner? (Bangkok Heart Hospital Equips with the state of the art 256 slice CT scanner)
- The 256-slice scanner produces high-quality images much faster and covers twice the area of a 64- slice CT scanner. It is very fast it can capture a three-dimensional image of the entire heart in just two heart beats compared to 10 beats with 64 slice CT.
- The 256 scanner incorporates technology that provides a more accurate and reliable test.
- Significantly reduce radiation exposure to the patient.
- Less problem with fast or irregular heartbeat.
- Do not require breath holding during the exam.
What is the difference between Coronary CTA, nuclear stress test and Exercise Stress Testing?
Coronary CTA directly demonstrates the anatomy of the heart and coronary arteries while nuclear stress testing indirectly diagnoses coronary disease by showing a difference in the distribution of a radioisotope in different parts of the heart muscle. It has less radiation than nuclear stress testing. Coronary CTA is more accurate than stress testing.
What are the clinical indications to have a Coronary CTA?
- To assess the condition of the coronary arteries
- To assess the patency (openness) of coronary artery bypass grafts
- To assess cardiac structure and morphology.
Are there any risks involved with the exam?
Coronary CTA is a very safe procedure; however, there are some minimal risks involved that are outlined below. If you have any specific questions our qualified professional staff can assist you.
- Intravenous contrast reaction: Rarely, patients may experience an allergic reaction to the intravenous contrast media used for the exam. The allergic reaction can be prevented by taking medication before the test. Patients should inform their doctor of history of allergies to food or medication.
- Patients with Kidney Disease: There is a risk associated with the intravenous contrast used for the exam in patients with compromised kidney function. Your doctor will order a simple blood test called BUN and Creatinine to establish normal kidney function required for the exam.
- Radiation exposure: There is a minimal risk with x-ray exposure and the amount is well below the level that can cause adverse effects. In addition, areas outside the heart are shielded to decrease the radiation dose. The benefit of the test far outweighs the risk of radiation exposure. The amount of radiation is usually lower than a nuclear medicine stress test.
- Pregnancy: X-ray may cause fetal birth defect.
What health conditions should you inform the doctor of before the test?
- Possibility of pregnancy
- Previous reaction to iodine
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Medications
- Claustrophobia
Is there any preparation for the test?
- Wearing: Loose-fitting clothing without metal fasteners, or hospital gown.
- Do not eat anything 3 hours prior to your appointment.
- Drink plenty of water to keep well hydrated before the test.
- Avoid caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea and soda as well as chocolate on the day of the exam.
- Take all your regular medications unless your doctor or nurse advise you otherwise.
- Do not take medications such as Viagra, Cialis or Levitra 12 hours before the test.
- Inform your doctor if you are pregnant or suspecting one. CTA exam use X-ray which may have effect on fetus, particularly during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Claustrophobia: You may discuss with your doctor whether you may need mild sedation during the coronary CTA exam.
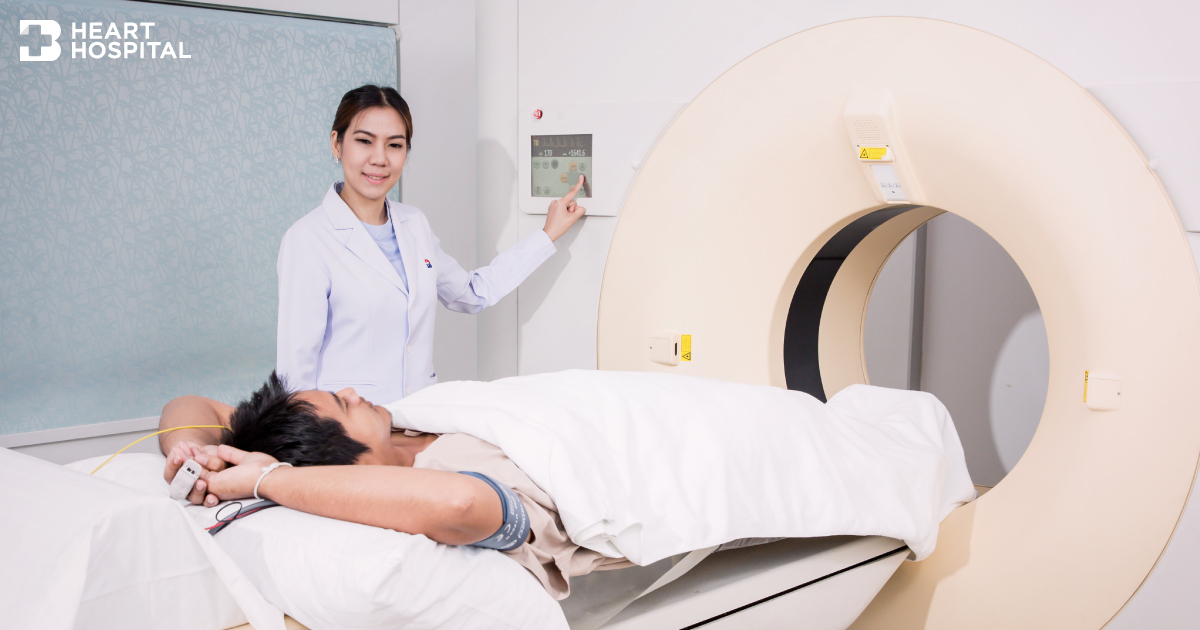
How is the procedure performed?
Coronary CTA examinations may be performed on outpatients or inpatients.
- You will be positioned on the movable examination table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain the correct position during imaging.
- You will be attached with electrocardiogram (ECG) leads, a respiratory gating belt, a small pulse monitor may be placed on your finger.
- You will be given breathing instructions and will be asked to hold your breath some times during the examinations.
- If a contrast material will be used in the CTA exam, there will be an intravenous line (IV). The contrast material will be injected into the IV line. There may be warm feeling when the contrast material was injected.
- Each imaging period is very short while the bed is sliding in and out.
How long does the procedure take?
And how soon you can get the result.
- It usually takes less than 30 minutes.
- There will be a process of imaging assembly. The test is usually reviewed by specially trained cardiologist or radiologist.
- Your primary doctor who orders the test will inform you the result.
After the test
If you have not been sedated, no recovery period is necessary. You may resume your usual activities and normal diet immediately after the exam.