MIS HEART | Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery

The heart is one of the most important organs in the entire human body. The common heart diseases are aortic aneurysm and valvular heart disease. These conditions are common in elderly and the incidence is rising in the middle aged population. With technological advancement, there is a new surgical technique called minimally invasive surgery. This surgical method requires much smaller incision and reduces pain and recovery time.

Aortic aneurysm – reducing the risk and hospital length of stay
Elderly, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cigarette smoking are known risk factors for aortic aneurysm. These can lead to a weak aortic wall that bulges outward, called aortic aneurysm. The common locations of aortic aneurysm are abdomen and thorax.
There are two primary methods of aortic aneurysm repair: open repair, and endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR). The open repair is a conventional open operation for the treatment of aortic aneurysm – to replace the diseased blood vessel with an artificial blood vessel. In endovascular aneurysm repair, two small vertical cuts are made in the groin and an artificial graft is delivered to and deployed from inside the aneurysm itself.
This is a new technique that is suitable for a high risk patient, as it is a less invasive procedure. Endovascular repair of aneurysms does not require a large incision and has a substantially shorter recovery time than the conventional open surgical approach. After the surgery, the patient need to be followed up yearly to make sure that the graft is in the right position and working properly.

Valvular heart disease – replacing an aortic valve without open heart surgery
Age related, or degenerative valvular heart disease, represents the most common etiology of aortic stenosis in the elderly population. It occurs when the heart’s aortic valve narrows. This narrowing prevents the valve from opening fully, which reduces or blocks blood flow from your heart into the main artery to your body and moving onwards to the rest of your body. When the blood flow through the aortic valve is reduced or blocked, your heart needs to work harder to pump blood to your body. With technological advancement, a cardiac surgeon is now able to perform a less invasive procedure to replace a narrowed aortic valve.
For people with aortic valve problems, the usual treatment is open heart valve surgery. However, for people who are too ill or who have many other medical problems such as diabetes and hypertension, open heart surgery may be considered too risky. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) or transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a procedure that allows an aortic valve to be implanted or replaced using a long narrow tube called a catheter. This new surgical technique is less invasive, reduces recovery time, and post-operative complications.
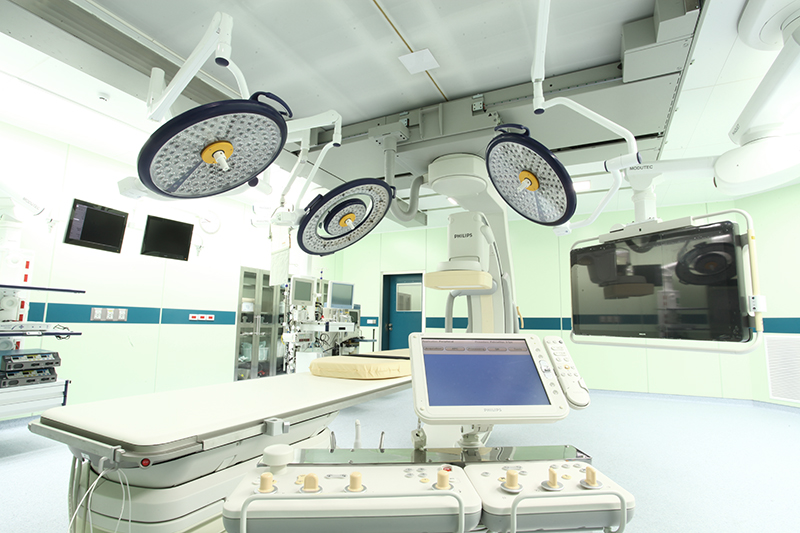
Fully functional hybrid operating room – designed to facilitate the most advanced cardiovascular procedures
Bangkok hospital’s hybrid operating room combines state-of-the-art surgical technology with the most cutting-edge imaging capabilities in one location. A hybrid operating room brings together advanced surgical facilities with the resources of a cardiac catheterization lab and expanded imaging capabilities. The combined facilities of a hybrid operating room provide doctors with the ability to perform interventional and surgical procedures at the same time.
At its core, a hybrid operating room combines advanced imaging capability with a fully functioning operating suite. The operating table can be fully adjusted to achieve optimal positioning. For optimal imaging technique, Flex Move Heart Navigator, provides high-resolution images, allowing surgeons to perform intricate procedures with extreme precision in less time. There is also a fluid management system which can deliver 6 liters of fluid per minute into a patient in order to replace blood loss thus stabilizing the blood pressure. A major advantage of the hybrid operating room is the combined resources and expertise allows for more rapid and tailored responses to unexpected complications. This can speed up surgical processes and improve patient safety.